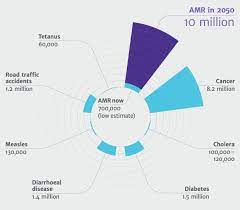
Amid worry over Antimicrobial Resistance, the World Health Organisation, (WHO) says it may lead to 10 million deaths by 2050 if urgent actions are not taken to reduce its burden.
The WHO also declared that AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity.
According to the Technical Officer of AMR at the WHO Nigeria Office, Dr. Laxmikant Chavan, while speaking at the Seventh Annual Conference of the Association of Nigeria Health Journalists in collaboration, held in collaboration with the WHO in Nasarawa State.
AMR is the ability of a microorganism (like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites) to change over time and no longer respond to medicines, making infections harder to treat, thus increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness, and death.
Chavan said AMR leads to increased costs to deliver health care, especially in the cost of newer expensive antibiotics and other drugs, cost of additional investigations, and causing extra length of stay at the hospital, among others.
According to him, “The cost of AMR to national economies and development is significant. Under a worst-case scenario, AMR could cause a reduction in Gross Domestic Product equal to that of the 2008 financial crisis.
“However, the economic impacts would be worse in lower-income countries and would likely last longer.
“AMR is putting the gains of Millennium Development Goals at risk and endangers the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals,” he said.
Chavan expressed worry over the increasing use of antimicrobial medicines, noting that the total global antibiotic consumption in humans, animals, and agriculture increased by 30% between 2000 to 2010, from 50 billion standard units to 70 billion standard units.
He said that the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials, lack of clean water, sanitation and hygiene, poor infection and disease prevention and control, poor access to quality, affordable medicines, vaccines, and diagnostics, lack of awareness and lack of enforcement of legislation are driving AMR globally, including Nigeria.





