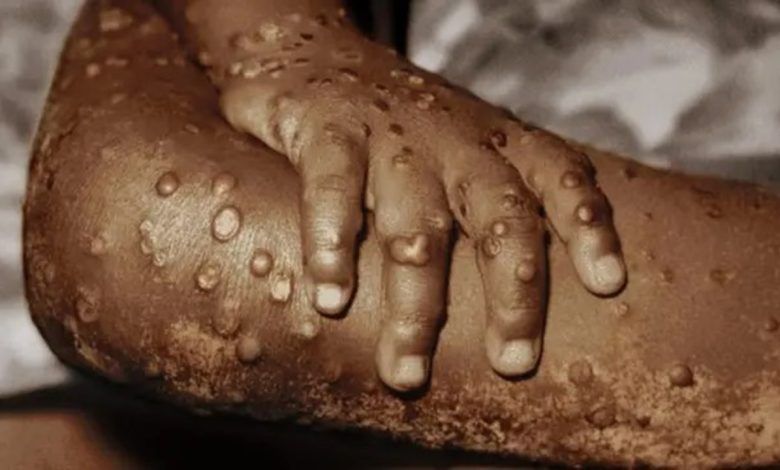
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has announced a bold target to halt mpox outbreaks in Africa within the next six months. This goal coincides with the anticipated arrival of the first vaccine shipments in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) in the coming days.
The DRC has been severely affected by the mpox outbreak, reporting over 18,000 suspected cases and 629 deaths. Despite this, Africa has received only a limited number of vaccines to combat the virus effectively.
During a press briefing, WHO Director-General, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, expressed confidence in achieving the six-month goal, highlighting the importance of strong government leadership and collaborative partnerships. Although mpox infections have surged across the continent, the mortality rate has remained relatively low.
A new strain of the virus, known as clade 1b, has been identified in several African countries, including Burundi, Cameroon, Rwanda, and Kenya. This variant, first detected in Congo in May, has raised concerns due to its potential for increased contagion.
In August, WHO declared mpox outbreaks a global emergency to catalyze a more robust international response. As part of the response, WHO estimates that approximately 230,000 vaccine doses could soon be sent to Congo and other affected regions. Additionally, the organization is launching educational campaigns to inform people in outbreak areas about prevention measures.
However, experts caution that the lack of comprehensive data on mpox transmission in Africa could complicate efforts to determine the most effective use of vaccines. Africa’s Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) aims to receive 380,000 vaccine doses from international donors, including the US and the EU, but this amount is still insufficient to fully eradicate the outbreaks.
The WHO’s six-month target reflects a significant push to contain the virus and prevent further spread, but the success of this effort will depend on the timely arrival of vaccines, effective public health strategies, and international support.





